Earthquake Strikes Norwegian Sea Near Svalbard Island: A Closer Look at recent Seismic Activity
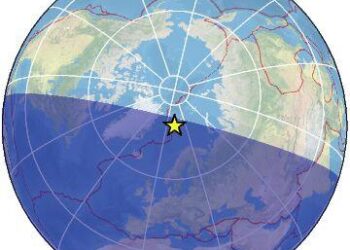
On March 5, 2025, a weak magnitude 2.9 earthquake occurred in the Norwegian Sea, approximately 30 kilometers northeast of Svalbard Island, part of the Svalbard and Jan Mayen archipelago. The tremor struck at 12:46 PM local time (GMT +1), drawing attention from seismologists and residents alike. While the quake is classified as minor, it highlights ongoing tectonic activity in this remote region, raising questions about the underlying geological processes at play. In this article, we will explore the implications of this seismic event, its potential causes, and how similar occurrences shape our understanding of the dynamic nature of the Earth’s crust in Arctic environments.
Overview of the Earthquake Event in the Norwegian Sea
A moderate earthquake occurred on March 5, 2025, in the Norwegian sea, approximately 30 km northeast of Svalbard Island, Svalbard and Jan Mayen. The seismic event registered a magnitude of 2.9 and struck at 12:46 pm local time (GMT +1). This earthquake is indicative of the tectonic activity prevalent in this polar region, where the interplay of the North American and Eurasian tectonic plates can lead to minor seismic events. Despite the moderate intensity, the event was closely monitored by geologists and seismologists due to the geographical significance of the area.
In the aftermath of the quake, no immediate reports of damage or casualties have emerged.However, the location of the earthquake raised interest in the scientific community for several reasons:
- Geological significance: Understanding the dynamics of tectonic plates in this region.
- Environmental Monitoring: Assessing potential impacts on unique Arctic ecosystems.
- Public Safety: Ensuring preparedness for future seismic activity.
| Date and Time | Location | Magnitude |
|---|---|---|
| March 5, 2025, 12:46 PM | 30 km northeast of Svalbard Island | 2.9 |
Geological Significance of the Svalbard Region
The Svalbard region is a dynamic and intriguing geological area that serves as a natural laboratory for understanding Earth’s processes. it is located at the junction of the North Atlantic and Arctic oceans, featuring a unique blend of geological formations due to its complex tectonic history. The region is characterized by:
- Glaciation: svalbard has been sculpted by glacial activity, resulting in fjords, mountain ranges, and deep valleys.
- Volcanism: The geological history includes periods of volcanic activity, notably on the adjacent Jan Mayen island, which provides insight into the volcanic processes of the North Atlantic region.
- Fossil Records: The deposits on the islands contain well-preserved fossils, offering valuable details about past climatic conditions and the biodiversity of ancient ecosystems.
additionally, the seismic activity, such as the recently recorded magnitude 2.9 earthquake, highlights the ongoing tectonic processes that continue to shape this remote area. These earthquakes serve as critical indicators of the underlying geological dynamics, which include:
- Plate Boundaries: The region lies near the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, where the Eurasian and North American tectonic plates converge.
- Research Opportunities: Continuous seismic monitoring provides scientists with data essential for understanding geological hazards and tectonic movements.
- Climate Change Impact: Changes due to climate phenomena, such as glacial retreat, also affect geological stability and landscape evolution.
Analyzing the Magnitude and Implications of a 2.9 Earthquake
The recent 2.9 magnitude earthquake off the coast of Svalbard, occurring at a depth of 10 kilometers, has raised questions among seismologists and residents alike. While this magnitude is classified as weak on the Richter scale, the geological implications of such tremors in the Norwegian Sea cannot be overlooked. Earthquakes in this region are generally indicative of ongoing tectonic activity, which may relate to the shifting boundaries of the North American and Eurasian tectonic plates. Although this particular quake did not cause meaningful damage or pose a tsunami threat, it serves as a reminder of the dynamic nature of the earth’s crust in polar regions, where geological processes continue to shape the landscape.
Analysis of seismic events, even those with lower magnitudes, provides valuable data for understanding larger patterns of tectonic movement. Factors to consider include:
- Frequency of Occurrences: How frequently enough do earthquakes of similar magnitude happen in the area?
- Potential for Larger Events: Is this seismic activity an indication of stress accumulation along fault lines that could lead to more significant earthquakes?
- Monitoring Changes: How can scientists leverage this data to improve early warning systems in vulnerable regions?
Monitoring tools and techniques are constantly evolving, allowing researchers to create more thorough risk assessments and preparedness plans. Events like this earthquake demonstrate the importance of continually observing and analyzing seismic activity, enabling communities in and around Svalbard to remain informed and vigilant regarding their geological environment.
Immediate Aftermath: Effects on Local Communities and Wildlife
The 2.9 magnitude earthquake that struck the Norwegian Sea, just 30 km northeast of Svalbard Island, left a mark on the local communities, prompting immediate assessments of both physical and psychological impacts. In nearby towns, residents reported mild shaking, causing some disruption but no major damage.However, the tremor served as a stark reminder of the region’s geological activity, igniting discussions about preparedness and emergency response protocols. Local authorities quickly organized community meetings to address concerns and provide information on how to handle future seismic events. The immediate effects included:
- Increased Stress levels: Many residents experienced heightened anxiety and a sense of vulnerability.
- Inspecting Buildings: Local officials initiated inspections of infrastructure to ensure safety and integrity.
- Emergency Services Mobilization: Teams were dispatched to monitor the area and engage with the community.
Wildlife in the vicinity also faced repercussions from the earthquake. The disturbance potentially impacted marine and terrestrial ecosystems, as vibrations traveled through water and soil, affecting animal behavior and migration patterns. Initial reports suggested that some marine species exhibited altered patterns, with fish and seals showing unusual surface behavior. Research teams were deployed to monitor these changes. The longer-term consequences on wildlife could include:
- Altered Habitats: Changes in seabed and coastal areas could affect nesting sites.
- Shifts in Food Sources: Disruption to local plankton blooms might affect feeding patterns of various species.
- Increased Monitoring: continued observatory efforts to understand the ongoing impacts on the region’s biodiversity.
Seismic Activity Monitoring: How the Event Fits into Current Trends
The recent magnitude 2.9 earthquake in the Norwegian Sea has drawn attention for its location, occurring 30 kilometers northeast of Svalbard Island. this seismic event is particularly significant within the context of recent geological trends observed in the Arctic region. environmental changes and shifting tectonic plates have heightened seismic activity across northern Europe, prompting scientists to closely monitor potential volcanic and tectonic interactions. Notably, the frequency of low-magnitude earthquakes in this area has increased, suggesting a dynamic geological environment possibly influenced by climate change and glacial movements.
Such seismic monitoring is critical for several reasons:
- Risk Assessment: Understanding seismic patterns helps assess risks for local populations and infrastructure.
- Volcanic Activity: Increased seismicity often signals volcanic unrest, necessitating environmental and safety precautions.
- Climate Interaction: Events like this reveal the intricate relationship between climate change and geological stability.
As monitoring efforts continue, seismic databases will be updated with real-time information, allowing scientists to analyze trends and develop predictive models. This collaborative research may shed light on not just Arctic geology, but broader tectonic dynamics shaping our planet.
Preparedness Recommendations for Residents in Earthquake-Prone Areas
Residents of earthquake-prone areas must prioritize safety and preparedness to minimize risks associated with seismic events. It is indeed essential to develop an emergency plan that includes designated meeting points and dialogue strategies for family members. Regularly practicing earthquake drills can significantly enhance readiness, ensuring that everyone knows how to react efficiently in the face of potential tremors. Additionally, it’s advisable to remain informed about local seismic activity through community resources or apps that provide real-time earthquake alerts.
Another key component of preparedness is ensuring your home is structurally sound and can withstand earthquakes. Consider the following measures to enhance safety:
- secure heavy furniture and appliances to walls to prevent them from tipping over.
- Install safety latches on cabinets to prevent contents from falling out during a quake.
- Create an emergency kit that includes water, non-perishable food, a flashlight, batteries, and first aid supplies.
| Item | Quantity |
|---|---|
| Water (1 gallon per person per day) | 3 days’ supply |
| Non-perishable food | 3 days’ supply |
| Flashlight with extra batteries | 1 |
| First aid kit | 1 |
Role of VolcanoDiscovery in Earthquake Reporting and Analysis
VolcanoDiscovery plays a crucial role in disseminating timely and accurate information regarding seismic events,including earthquakes like the recent magnitude 2.9 tremor reported in the Norwegian sea. This platform serves as a vital resource for scientists, researchers, and the general public by providing detailed analyses and updates on seismic activity. By leveraging cutting-edge technology and expert insights, VolcanoDiscovery enhances the understanding of tectonic movements and their potential implications, fostering a more informed global community.
In addition to real-time reporting, VolcanoDiscovery offers a comprehensive suite of tools and resources that facilitate in-depth analysis of seismic events. These include:
- Interactive maps: Visual representations of seismic data that help users comprehend the location and intensity of earthquakes.
- Data Archives: Access to historical records that allow for comparative studies and trend analyses.
- Expert Commentary: Insights from geologists and seismologists who elucidate the underlying causes of earthquakes.
Such features not only aid immediate response efforts but also contribute to ongoing research initiatives aimed at understanding earthquake dynamics better. By combining observational data with analytical tools, VolcanoDiscovery stands as a pillar in the realm of earthquake reporting and analysis.
Understanding the Svalbard Archipelago’s Seismic Geography
The Svalbard Archipelago, located in the Arctic Ocean, exhibits a unique seismic geography influenced by its location at the boundary between the Eurasian and North American tectonic plates. This geological setting contributes to a dynamic environment, where even minor seismic events, like the magnitude 2.9 earthquake that struck 30 km northeast of Svalbard Island, serve as reminders of the region’s tectonic activity. Such events, even though relatively weak, can provide valuable data about the ongoing geological processes that shape this remote part of the world. The complexities of the Svalbard Archipelago’s landscape are largely determined by both tectonic movements and glacial activity, creating a diverse array of geological features.
Understanding seismic activity in the region requires examining historical earthquake patterns and the role of volcanic systems that occasionally manifest beneath the ice. Key factors influencing seismicity in Svalbard include:
- Tectonic Activity: The interaction between tectonic plates generates stress and strain, leading to earthquakes.
- Glacial Movements: The melting and shifting of glaciers can trigger seismic events due to changes in pressure and weight on the crust.
- Volcanic Influence: Although less frequent, volcanic activity in the region can induce seismic waves and reshape the geological landscape.
Monitoring these geological phenomena is essential for understanding potential hazards and the implications they may have on local ecosystems and human activities. Efforts to study seismic geography in Svalbard continue to evolve,employing advanced technology to track even the slightest changes in this fascinating and complex environment.
Potential for Future Geological Events in the Region
The recent light earthquake off the coast of svalbard,measuring 2.9 on the Richter scale,serves as a reminder of the potential geological activity that this remote region may face in the future.This area, known for its unique geological features and proximity to tectonic plate boundaries, is prone to various seismic events. Factors contributing to this potential include:
- Active tectonic zones: The Norwegian Sea is influenced by the Mid-Atlantic Ridge,where the Eurasian and North American plates diverge.
- Volcanic activity: the region has a history of volcanic events, with nearby islands displaying signs of geothermal activity.
- Climate change: Melting glaciers may alter stress distributions in the Earth’s crust, potentially triggering earthquakes.
In assessing risks, it’s crucial for local authorities and scientists to monitor seismic patterns and geological shifts. Initiatives may include:
| Monitoring Techniques | Description |
|---|---|
| Seismographs | Installed across the region to detect and analyze tremors. |
| Remote sensing | Using satellite technology to observe land deformation and potential volcanic activity. |
| Geological surveys | Regular assessments to identify fault lines and potential hazards. |
By understanding the underlying geological dynamics, stakeholders can better prepare for future events, ensuring the safety and resilience of the community facing this ever-evolving natural landscape.
Expert Insights: What Seismologists Say About this Earthquake
seismologists have been closely monitoring the recent magnitude 2.9 tremor recorded in the Norwegian Sea, located approximately 30 kilometers northeast of Svalbard Island.While such a low-magnitude earthquake typically goes unnoticed by the general public, experts note that it provides an opportunity to study seismic activities in a region known for its geological complexity. According to Dr. Ingrid Holm, a leading seismologist, this event underscores the importance of understanding minor seismic events, which can offer valuable insights into regional tectonic processes and stress accumulation that may lead to larger quakes in the future.
The earthquake, which struck on Wednesday, March 5, 2025, at 12:46 PM (GMT +1), has not caused any significant damage or casualties. However, it serves as a reminder that the Arctic region’s geological activity is often influenced by various factors, including glacial movements and tectonic shifts. Key observations made by experts include:
- Depth of the quake: Shallow events are more likely to be felt but can provide crucial data regarding local fault systems.
- Connection to glacial isostatic adjustment: Experts are examining correlations between glacier movements and seismic activity in the area.
- Monitoring efforts: Increased monitoring in the region allows for better risk assessment and preparedness for future seismic events.
Public Awareness and Education on Earthquake Safety Practices
Public awareness and education are crucial components in mitigating the risks associated with earthquakes, especially in regions like Svalbard that may not regularly experience seismic activity. Community initiatives, schools, and local businesses can collaborate to create comprehensive awareness campaigns that inform residents about earthquake-prone zones, the significance of proper preparedness, and effective response strategies. Essential practices include:
- Creating an emergency kit: Stock essential supplies such as water, non-perishable food, a flashlight, batteries, a first-aid kit, and important documents.
- Developing a communication plan: Ensure all family members know how to reach each other and where to meet after an earthquake.
- Participating in drills: Engage in regular earthquake drills that simulate real-life scenarios, helping to instill confidence and a sense of readiness.
Educational programs should be tailored to cater to various demographics, ensuring that children, adults, and senior citizens all comprehend what to do before, during, and after an earthquake. Information can be disseminated through community workshops, online resources, and social media platforms. A useful table summarizing key safety actions can serve as a quick reference for residents:
| Timeframe | Recommended Actions |
|---|---|
| Before | Secure heavy furniture, check emergency kits, and stay informed about local risks. |
| During | Drop, cover, and hold on until shaking stops. Stay indoors if you are inside or move away from buildings and trees if outside. |
| After | Check for injuries, avoid damaged areas, and be prepared for aftershocks. |
In Conclusion
the recent weak magnitude 2.9 earthquake that struck the Norwegian Sea, located 30 kilometers northeast of Svalbard Island, serves as a reminder of the Earth’s ongoing geological activity, even in remote regions. Occurring on March 5,2025,at 12:46 PM (GMT +1),this seismic event was closely monitored by VolcanoDiscovery and highlights the significance of continuous observation in understanding the dynamics of our planet. While such minor earthquakes typically cause little to no damage, they contribute to our growing knowledge of tectonic processes and the potential for larger future events. As scientists continue to analyze this incident, it underscores the importance of public awareness and preparedness in areas prone to seismic activity. Stay tuned to VolcanoDiscovery for further updates and insights into seismic events around the globe.